The broad contrast between tissue sectors during the pandemic is well established, with AfH decline into Q1 2021 touching 20% for leading producers, with smaller players registering 30-40%. Here, AFRY Management Consulting Senior Consultant Olivia Ying and Analyst Navodya Denuwara look in detail at the five key end-use markets including food service, lodgings, healthcare, office building, and education and government to assess how, where and when the predicted recovery will occur.
Over the past decade, North America’s AfH tissue market has been leading the tissue demand growth at 2% per year compared to the annual growth rate of about 1% per year in the retail tissue market. This all changed when the Covid-19 pandemic shut down the AfH tissue market due to stay-at-home orders.
AfH tissue consumption hit a decade-low in 2020 at 2.6 million tonnes after an estimated 15% decline in consumption from 2019. While the AfH tissue market suffered from terrible demand in major end-use markets, the consumer tissue retail market thrived from customers who went on tissue hoarding sprees and panic buying hygiene products during the pandemic.
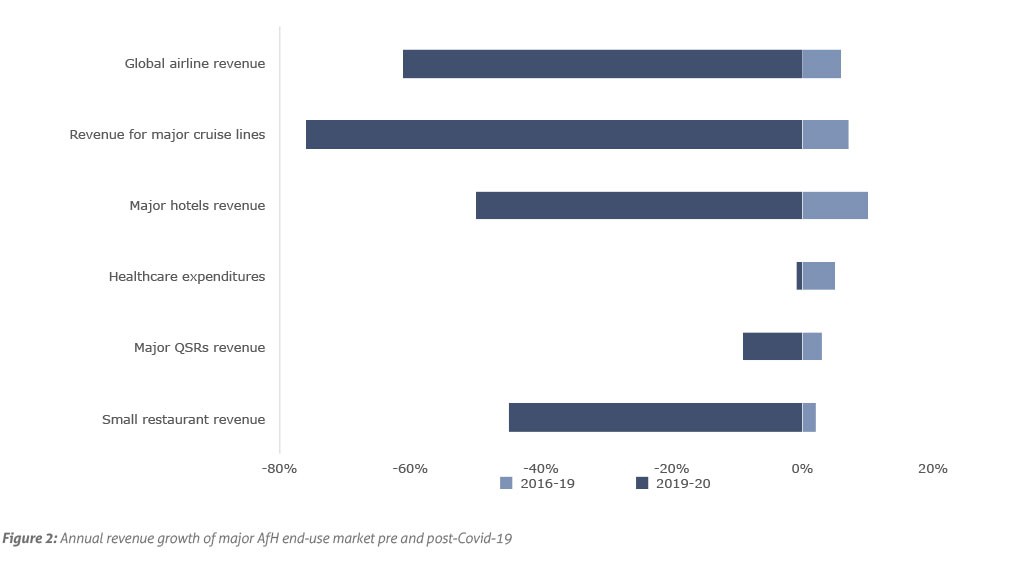
Leading North American tissue producers saw plummeting AfH tissue segment revenue and a decade-high At-Home tissue segment revenue in 2020 due to consumption shifts created by the stay-at-home orders. Tissue companies reported drastic sales declines for their AfH tissue segments. Kimberly-Clark, for instance, reported a 10% volume decline in its AfH category in 2020, which continued with an even higher reduction rate in Q1 2021 at -18%. Essity, another AfH tissue producer in North America, faced more than 20% decline in 2020 in its professional hygiene business mainly due to lockdowns and restrictions on outdoor activities and indoor dining. Some smaller market players witnessed drastic sales decline with a 15% decrease in AfH revenue in 2020, followed by a 30-40% decline in Q1 2021.
Short term consumption effects in both retail and tissue markets were very visible. However, the long-term effects of the pandemic are less known and discussed due to the various factors involved in growth outlook in the different market segments.
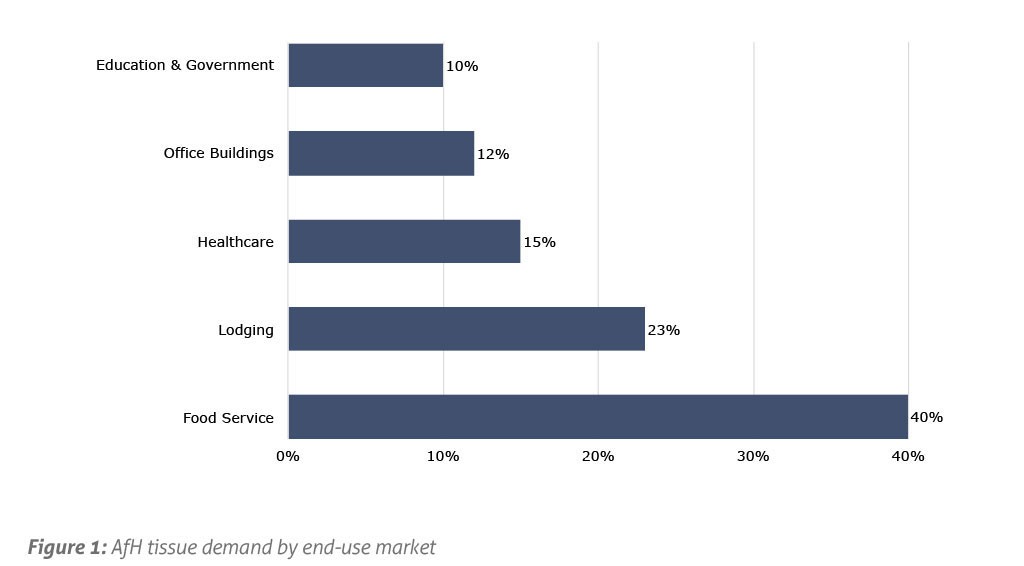
Overall, the North American AfH tissue market can be divided into five key end-use markets including food service, lodgings (airline, hotels, and cruises), healthcare, office building, and education and government [Figure 1]. We examined the past performance of each of these end-use sectors as well as compared current issues in each sector to determine what the recovery will look like for the AfH tissue market [Figure 2].
RECOVERY WITHIN THE LODGINGS INDUSTRY VARIES AMONG THE THREE MAJOR MARKETS
Among the main end-use markets, lodgings got hit the most by the pandemic as the major markets (airline, cruise line and hotel industries) suffered due to the lockdown. Total tissue consumption in the lodgings industry were down roughly 30-40% due to the sharp demand drop in consumers looking and willing and able to go on vacations. According to the International Air Transport Association, the airline industry experienced a 60% decline in 2020 from the 2019 level, and Cruise Line International Association reported a 70-80% decline in passenger travel in the cruise line industry. Leading hotels also reported a 50% decline in their 2020 revenue compared to 2019 level [Figure 2].
Within the lodgings industry, the hotels sector is expected to recover the earliest this year (2021), followed by cruises sector in 2022, and finally airlines in 2023/2024 thereafter. The current issue in airline recovery is whether a vaccine passport will be required to travel in the future. Most say that for domestic travel it is not expected to be required, however there is a large chance that for international travel it may be. Several issues accompany vaccine passports, one being the sheer distrust from the public about mandates from governments forcing for vaccination.
The second is that such passports might permanently limit travel by people who have yet to – and will refuse to – take the vaccine. Additionally, there is expected to be large differences in regional recovery for global airline travel because in strong domestic travel regions like the United States, airline travel will possibly rebound since passports may only be used within international regions. Due to this, regions such as Europe where travel is mostly international and not domestic, vaccine passports are expected to affect the recovery of the market.
As such, vaccination and government risk are expected to severely limit the ability of the airline industry to make a full recovery before 2023/2024.
In 2022, it is expected that cruise bookings will far outpace 2019 bookings because of future cruise credits. When cruises were suspended in 2020, passengers were given the option to get a full refund or a future cruise credit. Approximately half of cruise passengers that had their cruises cancelled chose a future cruise credit over a refund based on Carnival Cruise Lines. While 2022 sees a tremendous jump in expected cruise revenue, it will take until 2023 to get back to 2019 revenue levels. The current issue in the cruise industry also surrounds the use of vaccine passports because different states in the US are making these passports a state-level issue even though the initiative is a federal one.
The hotels industry had a less severe Coronavirus revenue drop compared to the airline and cruise line industries because hotels – if certain precautions are taken – can fall under Covid-19 safe travel. For example, it is possible for customers to avoid people that are not in their travel party relatively easily compared to cruises and airlines where the passengers would be enclosed in a confined space for a long period of time with no option to leave. Due to the appearance of relative safety, hotels fared better than airlines and cruises, even though they sustained a 50% loss in revenue during the pandemic. In the near future for hotel travel, consumers desire to stay closer to home, visiting destinations within easy driving distance such as cottages.
To accommodate this change in consumer preferences, large hotel chains will need to redirect their efforts to understand and engage with this new domestic, short-trip traveler. In this event, the hotels industry can recover their 2020 revenue loss relatively quickly in 2021.
STRONG DEVELOPMENT OF HEALTHCARE SECTOR CONTINUES
The healthcare industry remained strong during the pandemic. Government funding and Covid related spending offset much of the revenue loss in healthcare professional services (such as non-emergency surgeries like dental care, cosmetic, and others) due to the lockdown and fear of contracting Covid-19 in healthcare settings. This helped to result in only a 1% decline in overall healthcare expenditure in 2020.
While the sector itself experienced a relatively small decline compared to the other industries, an increase in virtual healthcare visits created a shift from AfH tissue consumption to the retail tissue segment. A survey by McKinsey in April 2020 found that the share of virtual visits out of total healthcare appointments significantly grew during the pandemic and surged from 11% in 2019 to almost 46% by mid-2020 and 76% of patients who used telehealth during Covid-19 said that they are likely to use it in the future, even post-Covid-19. The industry itself is expected to see a CAGR of approximately 5% growth each year from now until 2023. However, some say the growth will decelerate in spending due to emerging technologies, an ability to cure and prevent disease, and highly engaged consumers, while others say that spending will grow more than the expected 5% because of higher healthcare prices (not necessarily by amount of visits or patient numbers).
FOOD SERVICE REBOUNDS QUICKLY DRIVEN BY DEMAND SURGE
The food service industry saw a severe drop in 2020 due to massive lockdown and restricted capacity in indoor dining, although the booming food delivery business partially mitigated the revenue loss of the industry. During the pandemic, the food delivery business more than doubled the revenue in 2019.
Small to medium restaurants faced a more significant revenue drop, while major food chains and Quick Service Restaurants quickly adopted to food delivery services, which largely reduced the severity of the lockdowns and stay-at-home orders. Furthermore, single-use paper products started replacing cloth napkins and wipes at eateries due to health concerns.
There is also an additional issue with hand dryers in food service restrooms spreading bacteria and viruses through the hot air used in the dryer. These two factors contributed to the short-term change in tissue consumption in the food service industry, as Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggested paper products were better than cloth wipes and hand dryers for decontaminating surfaces. Overall, the restaurant industry is expected to recover in 2021 to 2019 levels.
OFFICE BUILDINGS AND EDUCATION GOES THROUGH STRUCTURAL CHANGES
Pandemic driven lockdowns also affected the office building, education, and government end-use markets through the trend towards remote working and online learning models. Tissue consumption shifted to the retail tissue market as people set up home workspace and took online courses which resulted in a 15-20% demand reduction.
Based on an AFRY survey in April 2021 of 600 US consumers, 60% of employees who worked from home during Covid-19 expect to do so post-Covid-19 after finding that their productivity levels stayed the same or increased while working from home. This generally positive reaction towards remote working is expected to contribute to a permanent decline in AfH tissue demand in office-buildings.
Interestingly, property specialists believe that more office space will be required in the future compared to what was required pre-Covid because of space and health requirements.
Post-Covid-19, only part of tissue consumption in the education industry is expected to return because of the move to homeschooling and online learning. The parents and students who took a liking to the current pandemic learning experience and found it suited their lifestyles may potentially choose to homeschool their children even after the education industry returns to the new normal.
Another contribution towards general decline in the industry is if the amount of online course options increases in the future for schools, a certain amount of
post-secondary students may be less willing to pay the same levels as prior years to attend school.
This will severely limit the number of students that go to colleges and universities in the US. What happens to the education industry in the future will rely on the students’ and parents’ willingness to shift to online learning, in effect replacing traditional schooling and forever changing the education landscape to digital for the future.
WHAT IS THE NEW NORMAL FOR THE AFH TISSUE SECTOR?
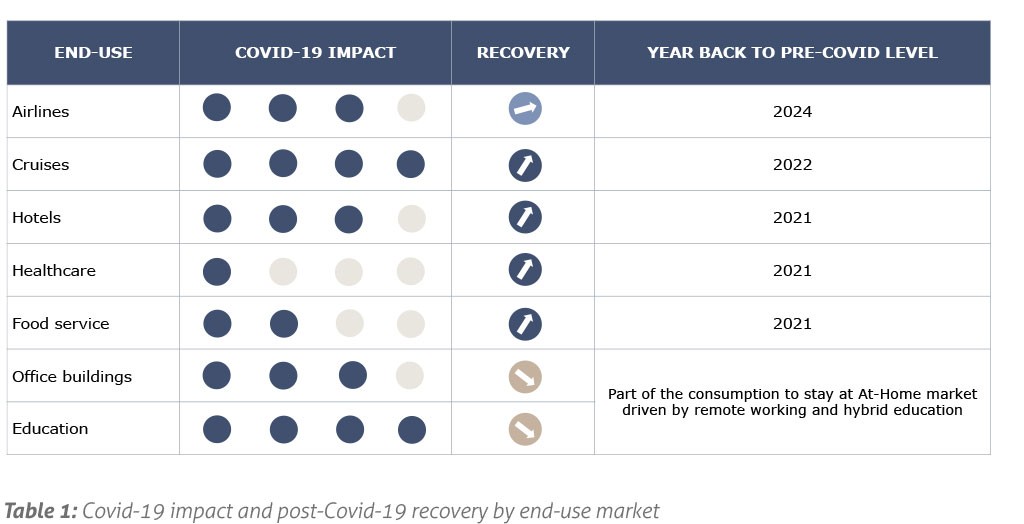
Major shifts have occurred across AfH tissue consuming end-use industries and the question now is whether they will recover to pre-Covid levels. Table 1 summarises the unevenness of the impact of the pandemic and the estimated post-Covid-19 recovery across major AfH end-use markets. The lodgings and food service industry are expected to make a comeback due to demand surge; the healthcare industry was not especially affected and so any recovery will be slight compared to the other end-use sectors; finally, the education sector and office buildings will most likely never recover due to the structural changes that occurred in consumer behavior and preferences.
This article was written for TWM by AFRY Management Consulting Senior Consultant Olivia Ying and Analyst Navodya Denuwara.